Actuator Types
Actuators play a fundamental role in many devices and processes across a wide variety of industries, they’re the “muscles” that carry out the action required by controlling a system. From household appliances to large industrial equipment, you could find actuators everywhere. They make our everyday systems automated and life easier. But what kinds of actuators are there? Are they all the same or do different systems require different types of actuators?
In this article, we are going to explore the various types of actuators, their features, their uses, and some important factors to consider when choosing an actuator. I hope you’ll find this article helpful whether you’re a seasoned engineer looking for a refresher or someone just starting to learn about actuators.
What Are Actuators?
Before we discuss the types of actuators, let’s quickly touch on what an actuator is. An actuator, in a simple explanation, is a device that manages to move or control a mechanism or a system. It’s responsible for performing the actual work ordered by a control system, thus being an integral part of any automated system^1^.
Different Types of Actuators
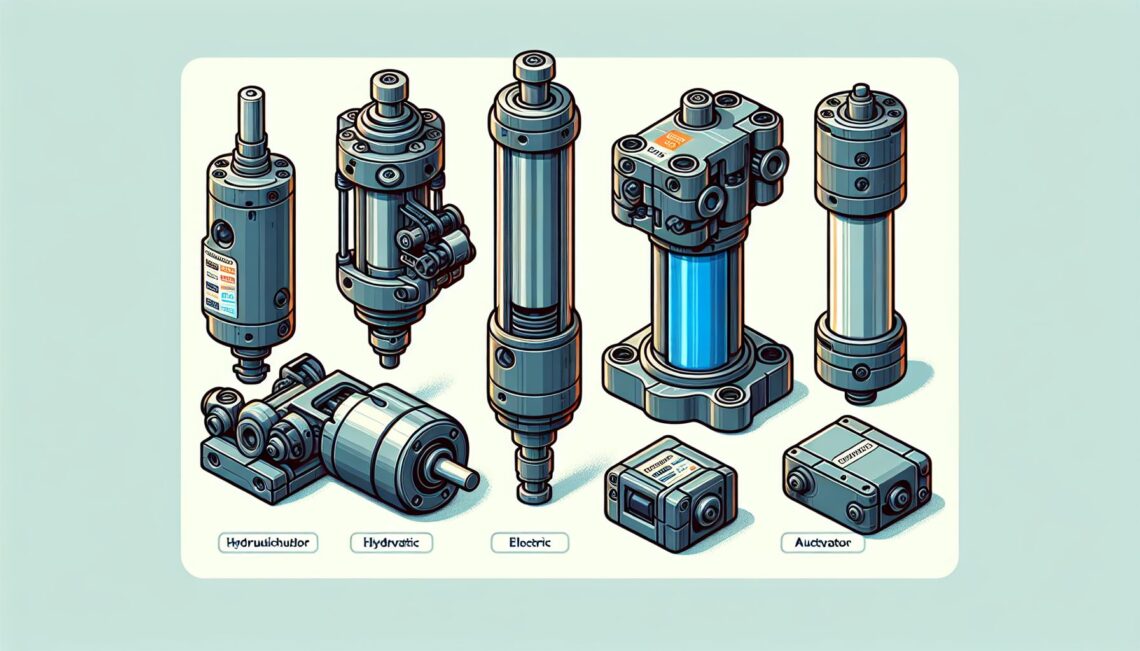
Actuators can be broadly classified into makes: mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electric, thermal or magnetic, and electronic. Let’s dive into a bit deeper on each of the actuator types.
-
Mechanical Actuators: These types of actuators function by converting rotary motion into linear motion. It’s carried out mostly via screws, gears, or others^2^.
-
Hydraulic Actuators: Hydraulic actuators function by converting fluid power into mechanical work. When hydraulic fluid is forced into a cylinder, this causes the rod and the load to move, which carries out the work. This is commonly used in heavy-duty industrial applications.
-
Pneumatic Actuators: Pneumatic actuators work on a similar principle as hydraulic actuators, but instead of hydraulic fluid, they use compressed air to affect motion. They are commonly used in industrial automation, HVAC control systems, and in some household applications.
-
Electric Actuators: They utilize the energy from a motor to generate force and motion. Electric actuators are becoming increasingly popular due to their high efficiency, programmability, and compliance with environmental regulations.
-
Thermal or Magnetic Actuators: These actuators leverage force from thermal or magnetic energy. They’re generally used in instances where a large change in temperature or a magnetic field is available to generate force.
-
Electronic Actuators: Find more and more applications with the rise of digital technology. As a subset of electrical actuators, these integrate electronic components to provide more advanced capabilities, such as programmability, network communication, and position feedback^3^.
With these many options, it’s critical to understand their distinctive capabilities, strengths, and weaknesses before selecting the right actuator type for a particular application.
Considerations When Choosing an Actuator
When choosing an actuator for a specific application, there are several key considerations to take into account. The application’s requirements and constraints will largely dictate the most appropriate type of actuator to use. Few factors to consider might include operation power, precision, efficiency, environmental condition compatibility, safety requirements, size, and cost.
Final Words
In conclusion, actuators are a crucial part of numerous systems around us. Understanding the different types of actuators and their specific uses can help us make more informed decisions when it comes to selecting and implementing an actuator in our project or system. I hope you found this introduction to actuator types valuable and informative.
Happy Learning!